International diversification is a method of spreading investment portfolios globally to reduce risk. Why do many experts recommend international diversification for long-term investors? In this article, we will explore the reasons in detail.
1. Understanding Deep Risk and Surface Risk
Investment risks can be broadly divided into two categories. The first is surface risk, which refers to short-term volatility. This is reflected in the daily price fluctuations of stocks or bonds, usually measured by standard deviation. The second is deep risk, which refers to long-term loss of purchasing power. This evaluates the real value of assets left in hand after accounting for inflation.
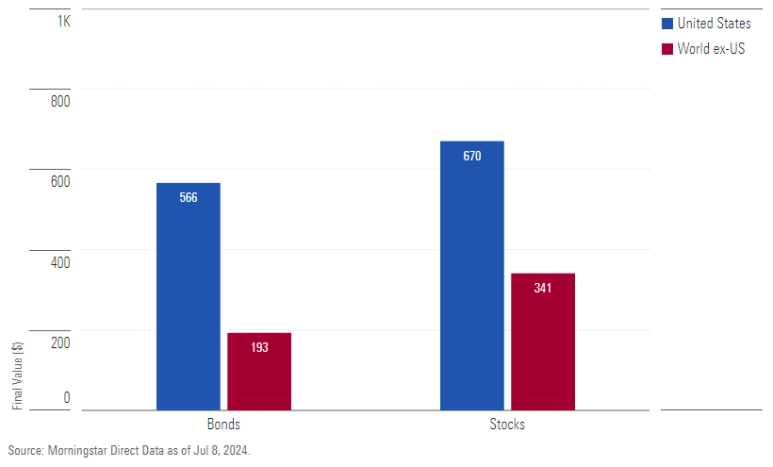
2. Deep Risk Analysis Through Historical Data
William Bernstein measures deep risk over several decades, and in this article, we will measure it on a decade-by-decade basis. For example, during the 10 years from 1949 to 1959, the worst real performance of U.S. bonds and stocks was observed. Bonds suffered significant value loss due to inflation, while stocks recovered after the Great Depression. On the other hand, foreign investments suffered substantial losses due to wars and economic instability.
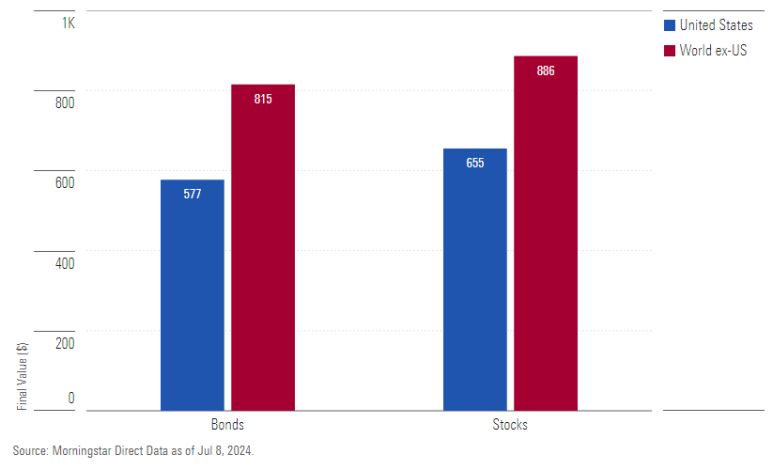
3. Modern Deep Risk Analysis
Data after 1950 shows that U.S. assets have generally delivered stable performance. In the last decade, U.S. stocks and bonds have delivered consistent returns despite inflation. Meanwhile, international investment assets have shown much better performance due to regional diversification. The growth of markets in Asia, particularly China, Japan, and India, has highlighted the benefits of international diversification.
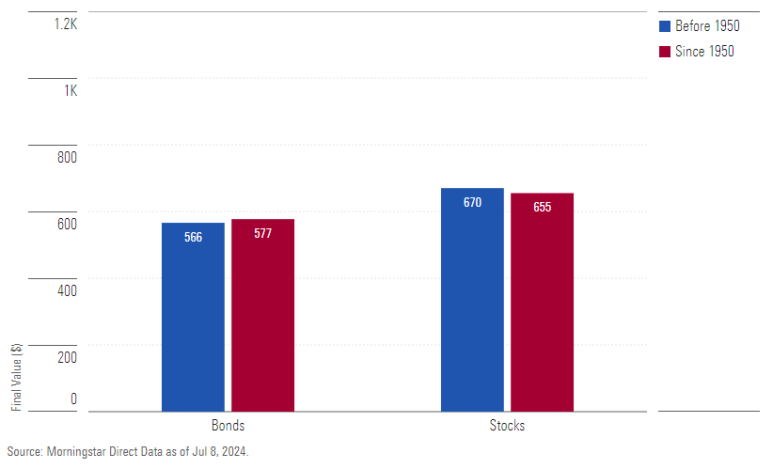
4. The Present and Future of International Diversification
Today’s international diversification has expanded beyond Europe to include regions like Asia, thanks to advancements in global communication and technology. Investors can now easily trade assets from anywhere in the world, significantly reducing portfolio risks.
For example, suppose an investor allocated 50% of their portfolio to U.S. stocks and 50% to Chinese stocks in the early 2000s. U.S. stocks experienced high volatility due to the IT bubble and financial crisis, while Chinese stocks enjoyed a high growth period. By diversifying across these regions, the investor could achieve more stable and higher returns.
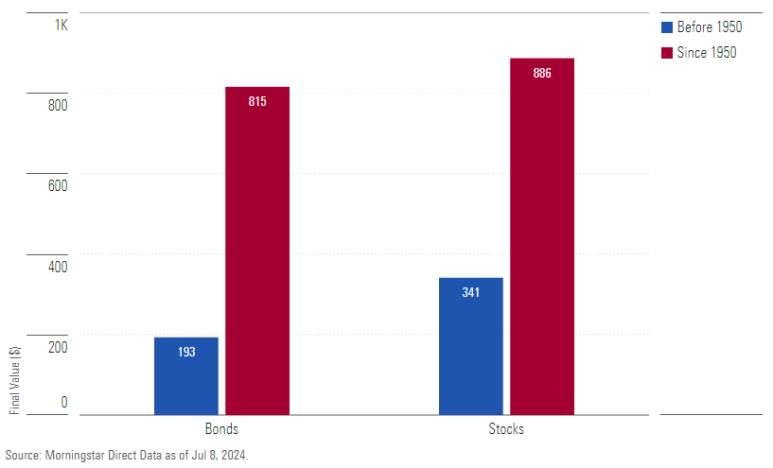
Conclusion
International diversification is an effective way to reduce long-term investment risks and achieve stable returns. By investing in assets from various regions alongside global economic changes, you can secure better financial stability. Consider diversifying your portfolio internationally for long-term financial stability and growth.
References: MorningStar, “Why International Investing Makes Sense for Long-Term Investors”
